Fast • Efficient • Streamlined — A New RNA Library Preparation Solution Empowering Precision Oncology
01 Overview of RNA-Sequencing
RNA-Sequencing (RNA-Seq) provides comprehensive characterization of gene expression profiles under different biological conditions and is widely used in expression profiling, alternative splicing and isoform identification, fusion and mutation detection, and allele-specific expression analysis. It has become an indispensable tool in basic biology, agricultural science, and clinical research. However, because ribosomal RNA (rRNA) constitutes the majority of total RNA, it frequently dominates sequencing reads and consumes valuable sequencing capacity. As a result, low-abundance transcripts and rare structural variants may fail to achieve sufficient coverage. To address this challenge, rRNA depletion, poly(A) enrichment, or targeted sequencing of specific genes/regions are commonly employed as essential strategies in RNA-Seq library preparation. In addition, compared with non-stranded libraries, stranded libraries preserve transcript orientation during workflow processing, enabling accurate discrimination between sense and antisense transcripts. This directional information is crucial for identifying overlapping genes, antisense transcripts, and novel transcripts.
With ongoing technological advancements and increasing demands for faster workflows, and operational simplicity Nanodigmbio introduces the NadPrep EZ RNA Library Preparation Kit—a rapid, flexible, and comprehensive solution designed for RNA-seq library preparation. The kit seamlessly integrates with both upstream and downstream modules to expand application scenarios, and it improves performance while reducing hands-on time and sequencing costs. Together, these features provide robust support for efficient and high-precision transcriptomic research.
02 RNA-Seq Library Preparation Solution
2.1 Introduction
NadPrep EZ RNA Library Preparation Kit is a rapid RNA library preparation kit developed for mainstream NGS platforms. It converts 2.5-500 ng RNA samples (cells, fresh tissues, blood, body fluids, microbes, FFPE tissues, etc.) into high-quality sequencing libraries. Applications include gene expression profiling analysis, single-nucleotide variant detection, alternative splicing and fusion gene analysis, allele-specific expression analysis, and RNA pathogen detection. This kit employs an optimized reaction system that integrates 2nd Strand cDNA Synthesis, End Repair & A-tailing into a single step, significantly shortening library preparation duration. This kit provides two types of 1st Strand Buffer and 2nd Strand & EA Buffer, allowing flexible preparation of non-stranded or stranded libraries. It is not only compatible with NadPrep rRNA Blocking Reagent or mRNA enrichment modules for transcriptomics sequencing, but also can be integrated with liquid hybrid capture systems for targeted RNA-Seq (RNACap), enhancing effective data output and reducing sequencing costs.
2.2 Workflow
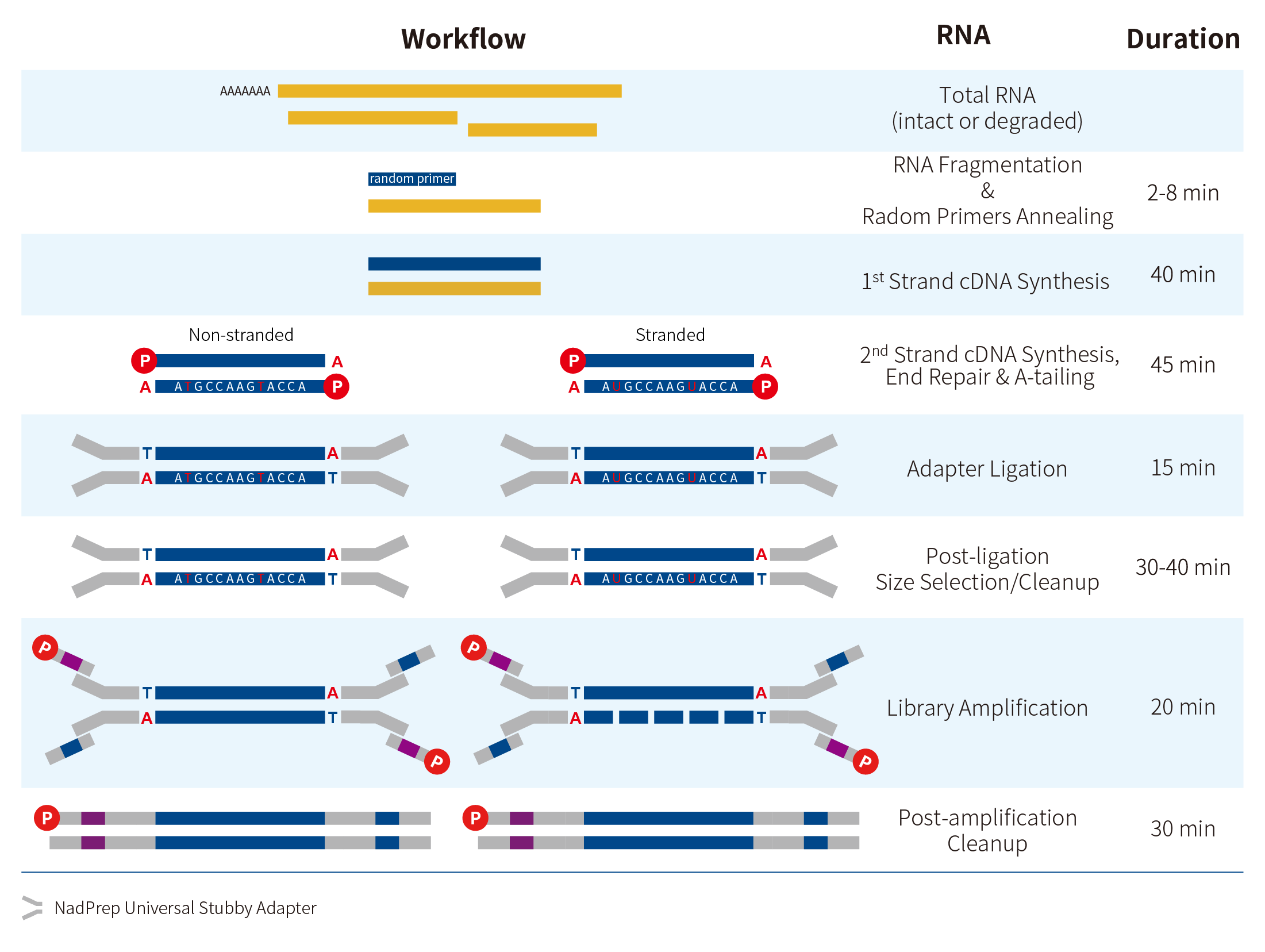
Figure 1. Workflow of non-stranded and stranded RNA-Seq libraries preparation using the NadPrep EZ RNA Library Preparation Kit.
2.3 Feature
Broad Coverage
-
Supports 2.5-500 ng initial input
-
Compatible with various sample types and qualities
-
Flexible choice of non-stranded or stranded library preparation
-
Adapters compatible with mainstream NGS platforms
-
Seamless integration with upstream and downstream modules for diverse applications
Fast Workflow
- Combines 2nd Strand cDNA Synthesis, End Repair & A-tailing into a single step
- Greatly streamlines the workflow and user-friendly operation, significantly shortens library preparation duration
Superior Performance
-
Higher library yield
-
More uniform transcript coverage
-
Higher detection sensitivity for low-abundance transcripts and fusion genes
-
Higher strand specificity;
-
Excellent library complexity
03 Application Scenario Example — Connection with RNACap
3.1 Targeted RNA-Seq: The Versatile “Intelligence Officer” in Precision Oncology
Tumor-related genetic alterations mainly include single-nucleotide variants (SNVs), insertions and deletions (Indels), amplifications (Amp), and gene fusions. With the advancement of precision medicine, comprehensive profiling of these alterations has become a critical component of cancer diagnosis and therapeutic decision-making for both targeted and immunotherapy. NGS-based molecular diagnostics significantly improve diagnostic accuracy, refine prognostic assessments, and guide the selection of therapeutic targets.
Traditionally, DNA-Seq has served as the main approach for mapping tumor genomic alterations. However, it still faces notable limitations in certain situations. For example, long intronic regions may not be adequately covered by probes, and repetitive sequences at breakpoint sites can interfere with bioinformatic analysis. These challenges make it difficult for both whole-genome sequencing and targeted DNA sequencing to capture specific regions effectively. In contrast, RNA-Seq—a competent “intelligence officer”—directly analyzes functional transcripts, bypassing intron interference. This allows for more accurate detection of clinically meaningful transcriptomic events, greatly improving sensitivity. As a result, RNA-Seq provides substantial value in fusion detection, variant identification, splice-site validation, and expression analysis, all of which can directly influence patient diagnosis and treatment paths [1–2].
Of course, there are also some concerns regarding the use of RNA-Seq in oncology. First, RNA from FFPE samples is prone to degradation and generally less stable than DNA, potentially affecting result reliability. Second, some also believe RNA-Seq may be less effective in detecting certain SNVs/Indels. Moreover, if both DNA-Seq and RNA-Seq are performed in the clinic to separately detect point mutations and fusion variants, then total testing cost, tissue requirements, and turnaround time (TAT) will increase—posing challenges especially for small biopsies with limited available tissue. Notably, studies have shown a high concordance (approximately 93.3%) between DNA-Seq and RNA-Seq for SNV/Indel detection [2]. Meanwhile, RNA-Seq can generate multidimensional data—including point mutations, fusions, splicing events, and expression profiles—within a single assay.
Additionally, RNACap significantly enhances sequencing coverage depth across target regions by enriching genes or regions of interest, thereby improving the sensitivity for detecting low-abundance transcripts and fusion genes. As the technology continues to mature, RNACap has strong potential to evolve into a true “all-in-one solution” for tumor molecular diagnostics—lowering testing costs, reducing tissue requirements, shortening turnaround time, and addressing clinical pain points such as tissue exhaustion, high costs, and prolonged waiting periods. This advancement provides a promising new pathway for precision oncology.
3.2 Nanodigmbio's RNACap End-to-End Solution
For cancer diagnostics and targeted/immunotherapy studies, Nanodigmbio offers a complete end-to-end RNACap solution. This includes high-efficiency RNA library preparation reagents, ES hybrid capture reagents, and validated, ready-to-use commercial panels designed for a variety of applications:
Solid tumor fusion detection: OncoFu Elite (for RNA) Panel v1.0
Hematologic malignancy fusion detection: NanoHema Panel v2.0
Immune repertoire diversity analysis: IGTR Panel v1.0
Together, these modules provide robust technical support for personalized precision diagnostics and treatment.
3.3 Performance
3.3.1 Compatible with a Wide Range of Input Amounts
The NadPrep EZ RNA Library Preparation Kit supports a wide range of input amounts—from 2.5 to 500 ng of total RNA—enabling high-quality library preparation across various sample types. To evaluate its performance, RNA extracted from the cell line (Takara, 636530) was used as input at different concentrations. Libraries were prepared using the NadPrep EZ RNA Library Preparation Module coupled with the NadPrep Universal Stubby Adapter (UDI) Module (NovaSeq) and NadPrep Universal Adapter (MDI) Module (for MGI) (DNBSEQ) respectively. The results showed that both non-stranded libraries and stranded libraries achieved the expected yields across all tested input amounts (Figure 2), fully meeting the downstream library requirements for hybrid capture.
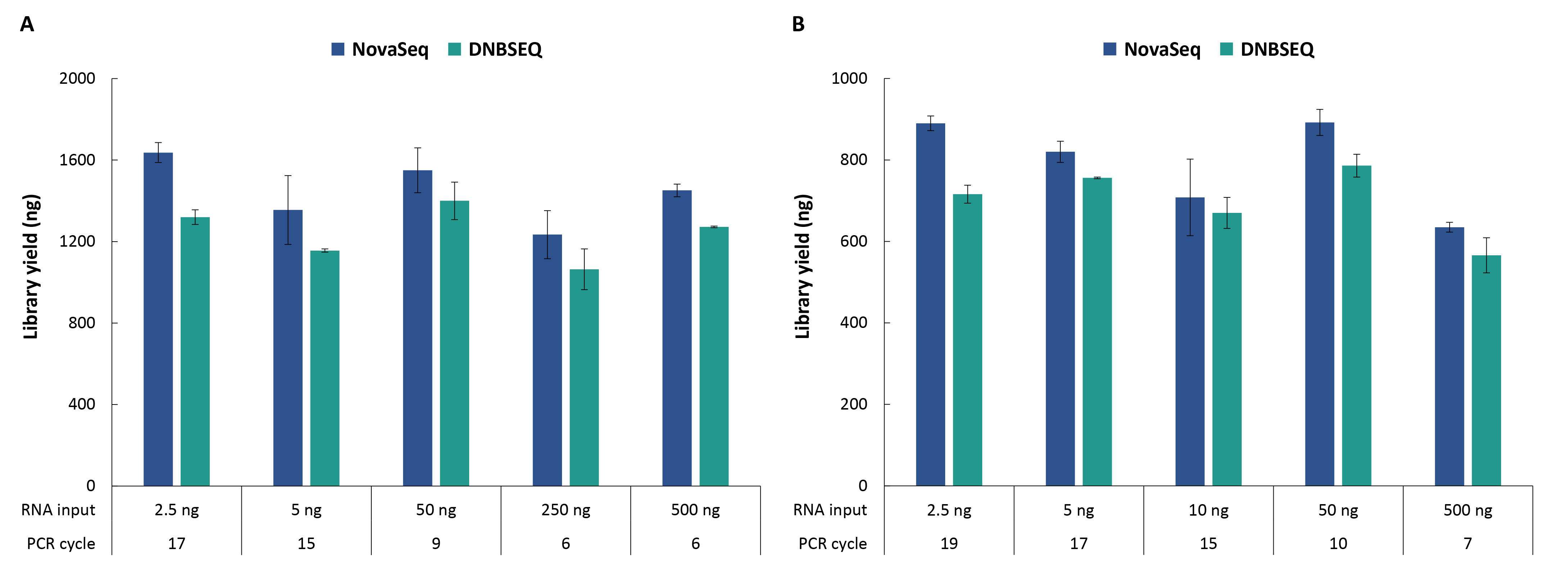
Figure 2. Library yield for cell line RNA samples with different input amounts. A. non-stranded libraries; B. Stranded libraries.
3.3.2 Compatible with Multiple Types Samples of Different Grades
The NadPrep EZ RNA Library Preparation Kit offers broad sample compatibility and supports efficient library preparation from RNA samples of different grades. Using 50 ng of cell line RNA and FFPE-derived RNA as inputs, the results showed that the kit achieved the expected library yields for both high-quality cell line RNA and lower-quality FFPE RNA samples (Figure 3). These consistent outputs provide reliable support for subsequent hybrid-capture workflows.
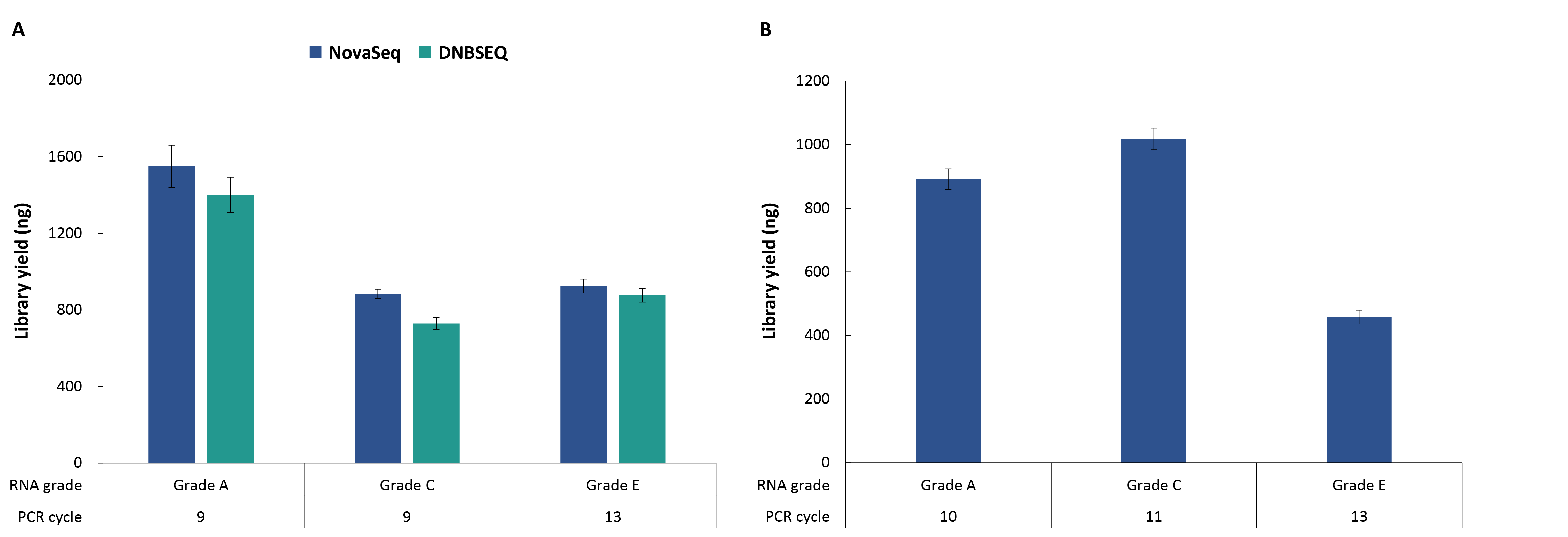
Figure 3. Library yields from RNA samples of different grades using the NadPrep EZ RNA Library Preparation Kit. A. non-stranded libraries; B. Stranded libraries.
Note: Sample grading standard | Grade A (cell line RNA): Human Brain Total RNA (Takara, 636530), RIN ≥ 7; Grade C (FFPE-derived RNA): DV200 ≥ 50; Grade E (FFPE-derived RNA): DV200 < 50.
3.3.3 More Efficient Library Yield
We further evaluated library preparation efficiency using 50 ng of RNA samples across different quality grades. Libraries were prepared with the NadPrep EZ RNA Library Preparation Module and compared against Vendor A/C & B using the NadPrep Universal Stubby Adapter (UDI) Module. The results demonstrated that NadPrep achieved higher library yields with fewer amplification cycles compared to Vendor A/C & B, indicating superior library preparation efficiency (Figure 4).
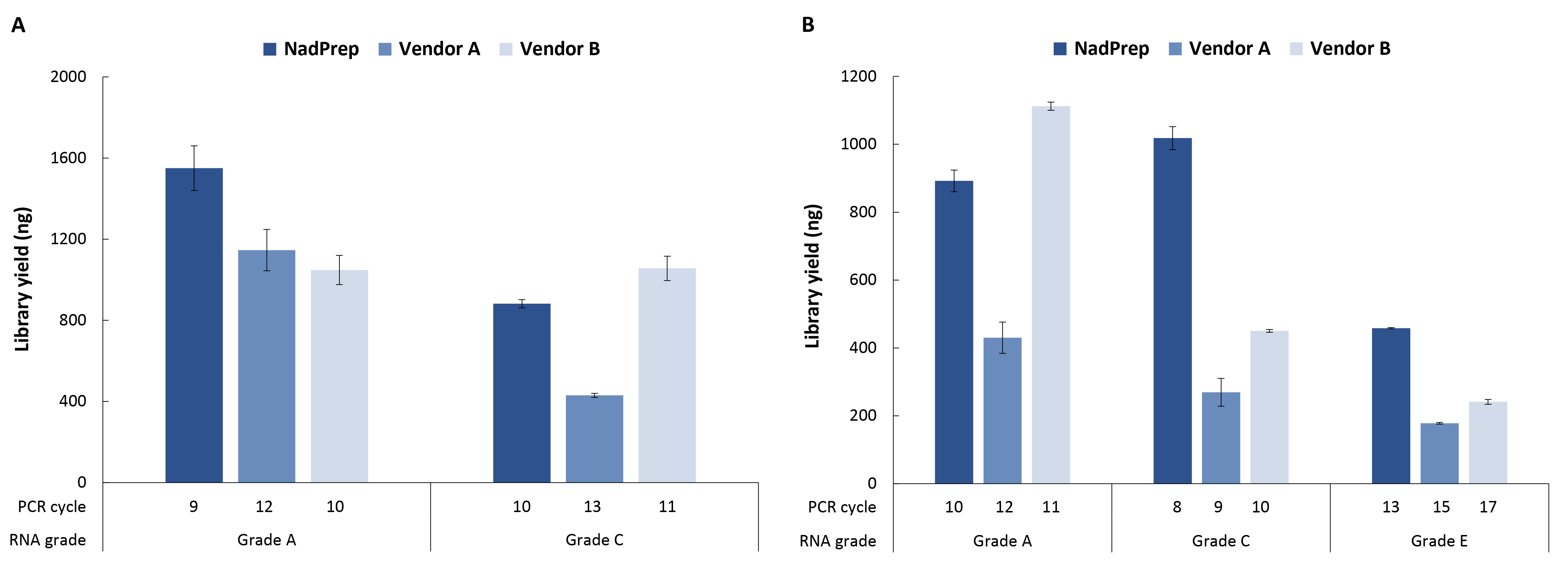
Figure 4. Nadprep EZ RNA Library Preparation Kit has a more efficient library yield than Vendor A & B. A. non-stranded libraries; B. Stranded libraries.
3.3.4 More Uniform Transcript Coverage
To assess the basic performance of the RNACap workflow, pre-libraries were prepared from RNA samples of varying quality, and 500 ng of each pre-library was used for hybrid capture with the NanOnco Plus Panel v2.0 and NadPrep Hybrid Capture Reagents. The results demonstrated that both non-stranded and stranded libraries prepared with NadPrep exhibited significantly more uniform transcript coverage compared to Vendor A/C & B (Figure 5). This uniformity is critical for ensuring data accuracy and for detecting low-frequency variants. 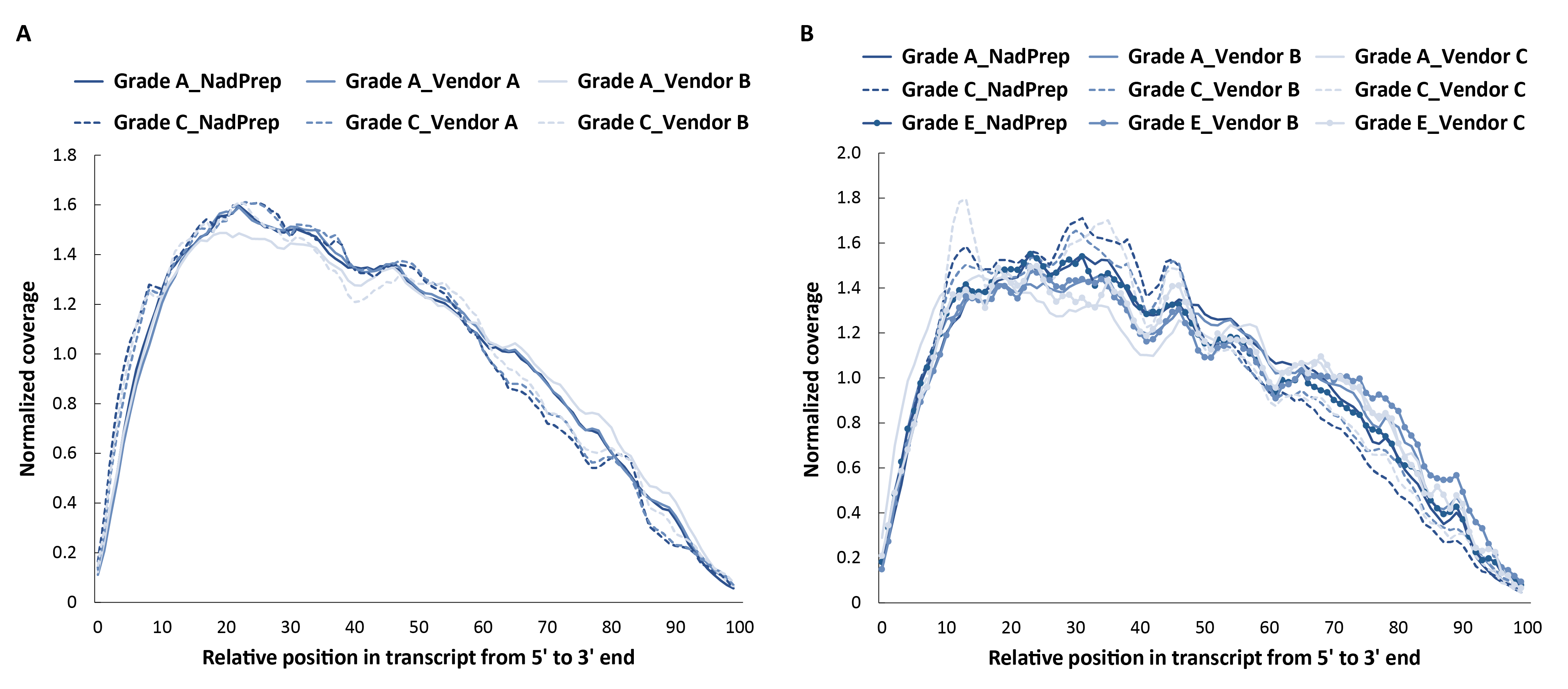
Figure 5. NadPrep EZ RNA Library Preparation Kit performs more uniform transcript coverage compared to the Vendor A/C & B. A. non-stranded libraries; B. Stranded libraries. Sequencing was performed on NovaSeq 6000, PE150. For each sample, 0.3 Gb of sequencing data was randomly selected for data analysis.
3.3.5 Higher Strand Specificity
In strand-specificity assessment, over 98% of reads generated from NadPrep-prepared libraries aligned to the expected orientation strand, demonstrating excellent strand specificity. The performance of NadPrep was comparable to Vendor B and significantly superior to Vendor C (Figure 6).
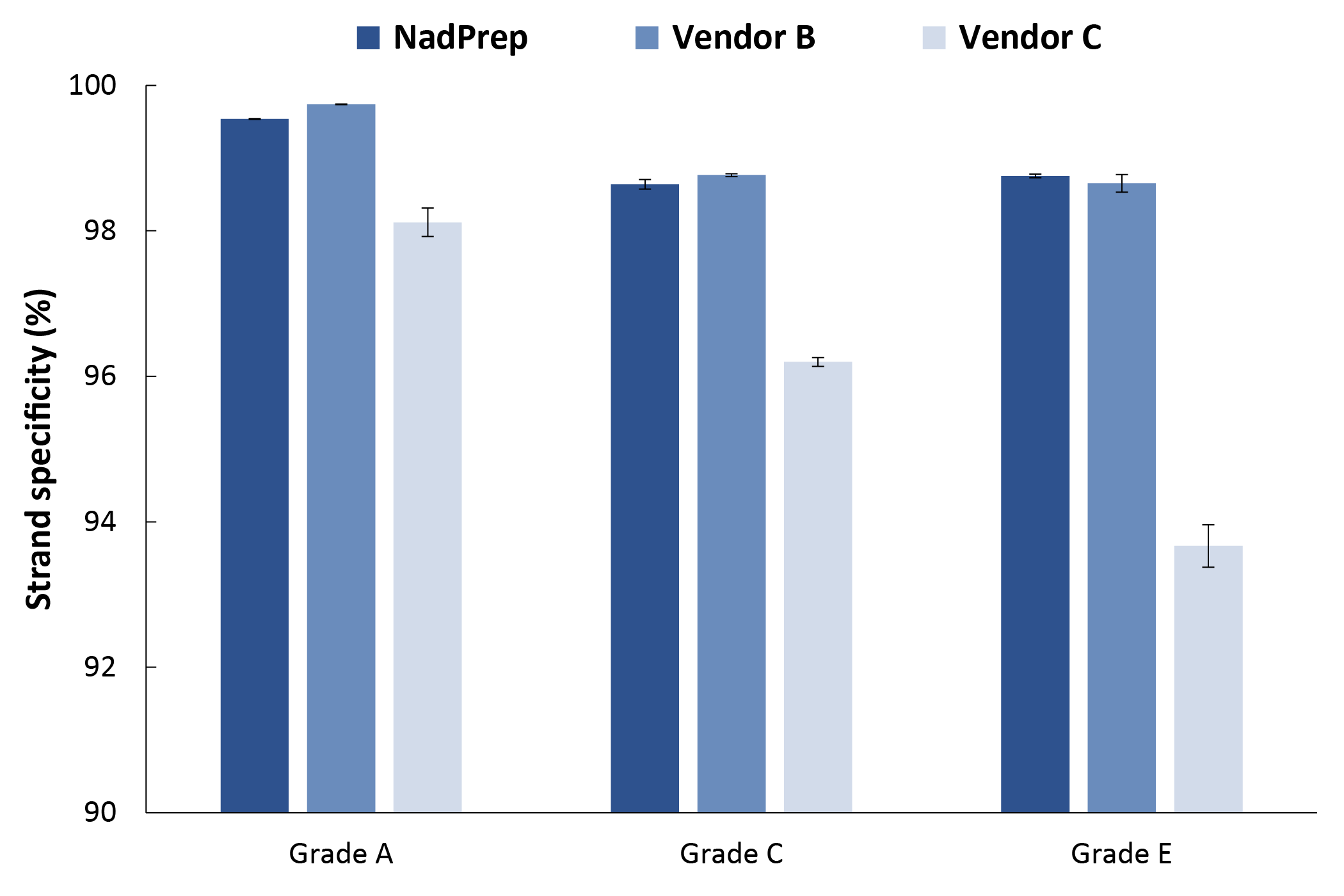
Figure 6. NadPrep EZ RNA Library Preparation Kit performs higher strand specificity with RNA samples across different grades.
3.3.6 Higher Detection Sensitivity
To evaluate the detection of low-abundance transcripts, 50 ng of cell line RNA was spiked with 1 μL of exogenous ERCC standards (1:1,000) and used to prepare non-stranded pre-libraries. Hybrid capture was performed using the Ext-RNA Control Panel v1.0 and NadPrep Hybrid Capture Reagents. The results showed that NadPrep detected a higher number of ERCC transcripts (Figure 7. A) and the lower limit of detectable copy number was significantly reduced (Figure 7. B), demonstrating its superior sensitivity for low-abundance transcripts.
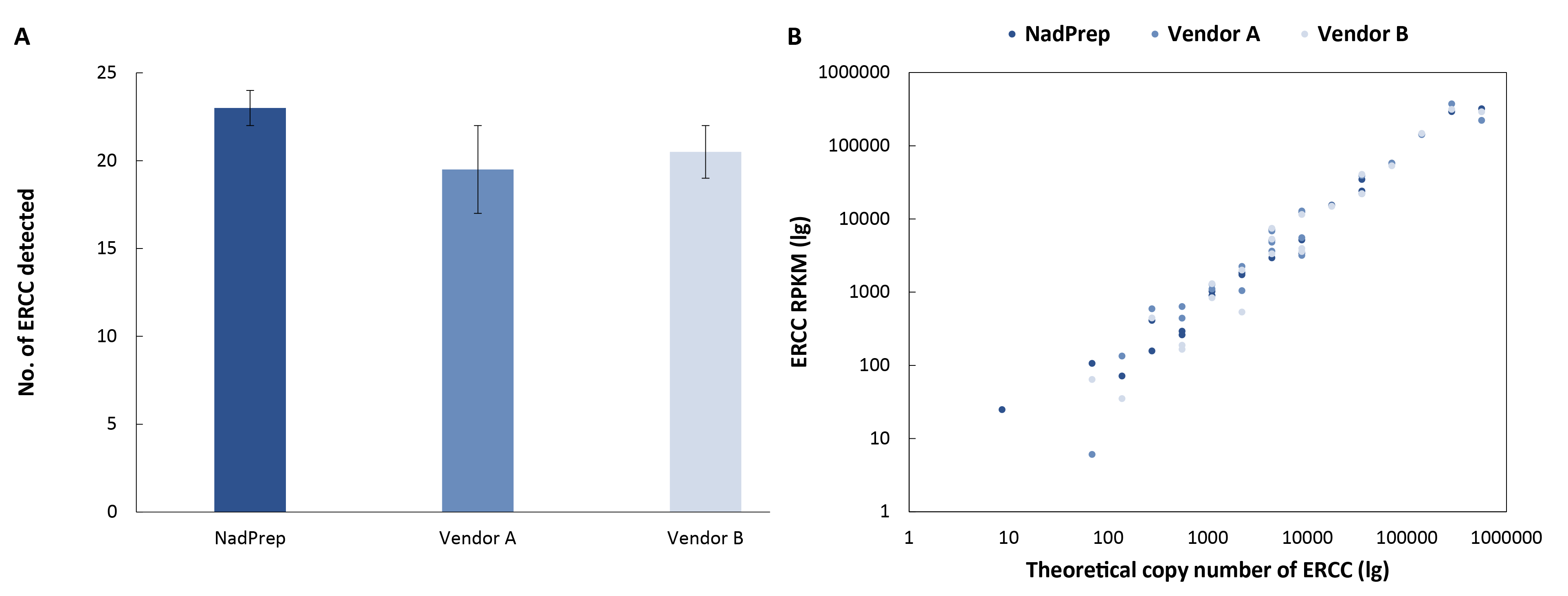
Figure 7. NadPrep EZ RNA Library Preparation Kit performs higher sensitivity for low-abundance transcripts compared to Vendor A & B. A. No. of ERCC detected; B. ERCC RPKM.
In addition, fusion gene detection performance was evaluated using 100 ng of FFPE-derived RNA (Grade C) spiked with 3.125% tumor fusion multi-locus FFPE standards (DNA/RNA) (GeneWell, GW-RPSM1006) to prepare non-stranded pre-libraries. Hybrid capture was performed with the OncoFu Elite (for RNA) Panel v1.0 and NadPrep Hybrid Capture Reagents. The results showed that libraries prepared with NadPrep and Vendor A detected 100% of all fusion genes covered by the panel, whereas Vendor B missed three fusion loci. Moreover, NadPrep generated a significantly higher number of unique reads supporting fusion events compared to Vendor A & B (Figure 8), further highlighting its advantages in fusion detection.
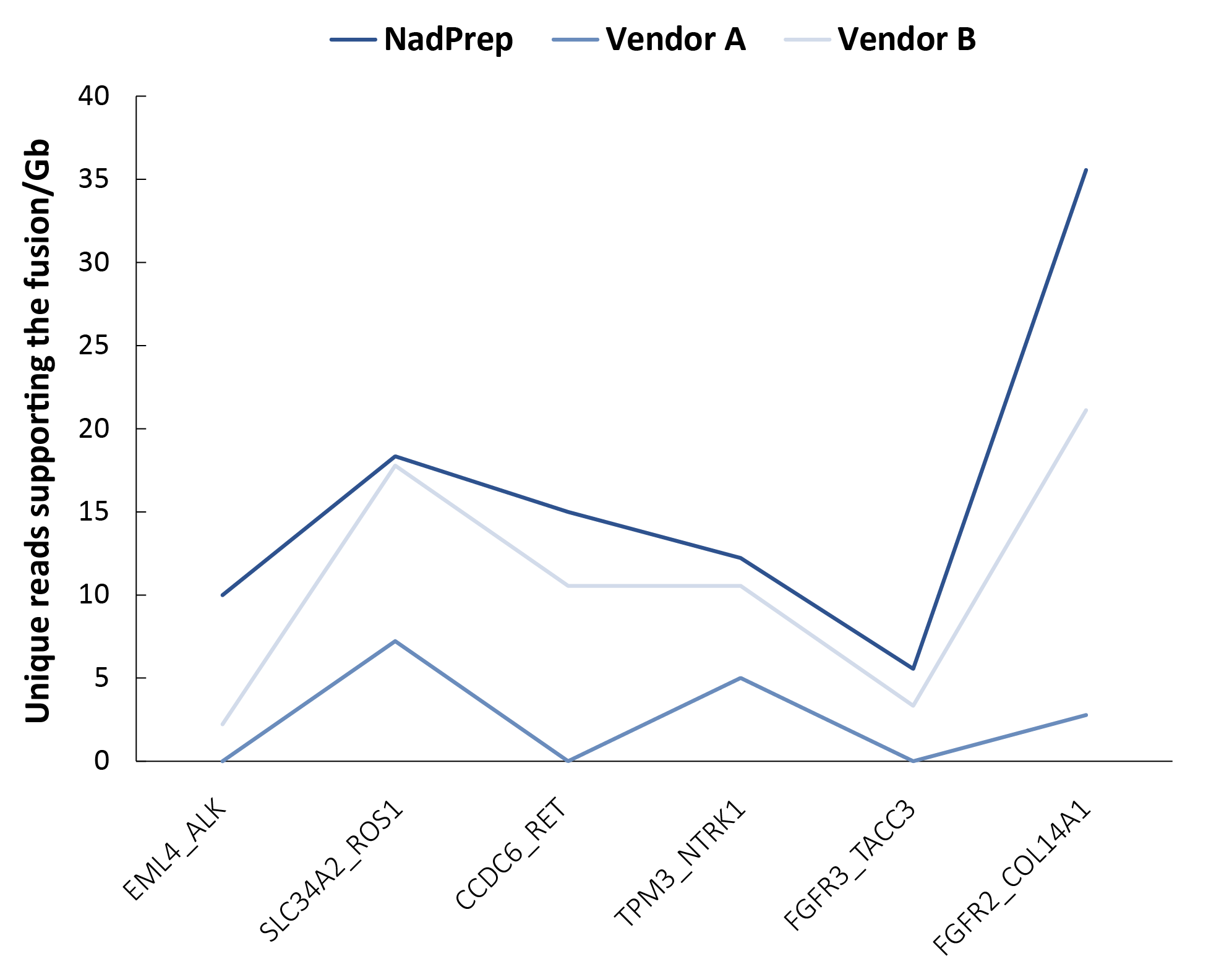
Figure 8. NadPrep EZ RNA Library Preparation Kit performs higher detection sensitivity for fusion gene than Vendor A & B in standards.
04 Summary
Compared with DNA-Seq, targeted RNA-Seq offers greater sensitivity and specificity for the detection of low-abundance transcripts and fusion genes. It also enables direct assessment of the functional impact of splice-site mutations at the transcript level. This approach combines high detection performance with broad applicability, maintaining high success rates even with severely degraded FFPE RNA samples. Furthermore, targeted RNA-Seq can significantly reduce testing costs, enhancing clinical feasibility.
The newly launched NadPrep EZ RNA Library Preparation Kit streamlines the experimental workflow and improves operational convenience. When combined with targeted capture strategies, it further enhances detection sensitivity, providing a reliable solution for gene expression analysis, low-abundance transcript detection, and fusion gene identification. It is particularly well-suited for rare or degraded clinical samples commonly encountered in practice.
Reference
[1] Center P Q C. Expert consensus on combined DNA and RNA next-generation sequencing of common driver genes in solid tumors (2025 version) [J]. Zhonghua bing li xue za zhi= Chinese journal of pathology, 2025, 54(7): 701-709.
[2] Siddaway R, Glembocki A I, Arnoldo A, et al. Clinical utility of targeted RNA sequencing in cancer molecular diagnostics[J]. Nature Medicine, 2025: 1-10.
Solutions
- Methyl Library Preparation Total Solution
- Sequencing single library on different platform--Universal Stubby Adapter (UDI)
- HRD score Analysis
- Unique Dual Index for MGI platforms
- RNA-Cap Sequencing of Human Respiratory Viruses Including SARS-CoV-2
- Total Solution for RNA-Cap Sequencing
- Total Solution for MGI Platforms
- Whole Exome Sequencing
- Low-frequency Mutation Analysis
Events
-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Boston 2025 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG)

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio Invites You to Join Us at WHX & WHX Labs Kuala Lumpur 2025, Malaysia International Trade and Exhibition Centre in Kuala Lumpur

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio Invites You to Join Us at Hospitalar 2025, Brazil International Medical Device Exhibition in São Paulo

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Denver 2024 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG)

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Sapporo 2024 Annual Meeting of the Japan Society of Human Genetics (JSHG)

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Association for Diagnostics & Laboratory Medicine (ADLM)