Breaking news! A Nipah virus outbreak alert has resurfaced in India, and Nanodigmbio’s precision testing solution has rushed in to provide rapid support.
In recent days, multiple regions in India have reissued alerts for the Nipah virus (NiV) outbreak. As confirmed cases continue to rise, reports of hospital-acquired infections and healthcare worker exposure have drawn heightened attention across the global public health community.
As a zoonotic virus with a fatality rate of 40%–75%, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), and with no specific vaccine or therapeutic drug currently available, Nipah virus control and prevention rely heavily on rapid, accurate pathogen detection. Nanodigmbio closely monitors emerging and re-emerging infectious disease developments worldwide. Leveraging its robust targeted sequencing technologies and end-to-end automated platforms, Nanodigmbio has responded promptly to Nipah virus testing and outbreak-tracing needs, providing reliable technical support for epidemic prevention and control.
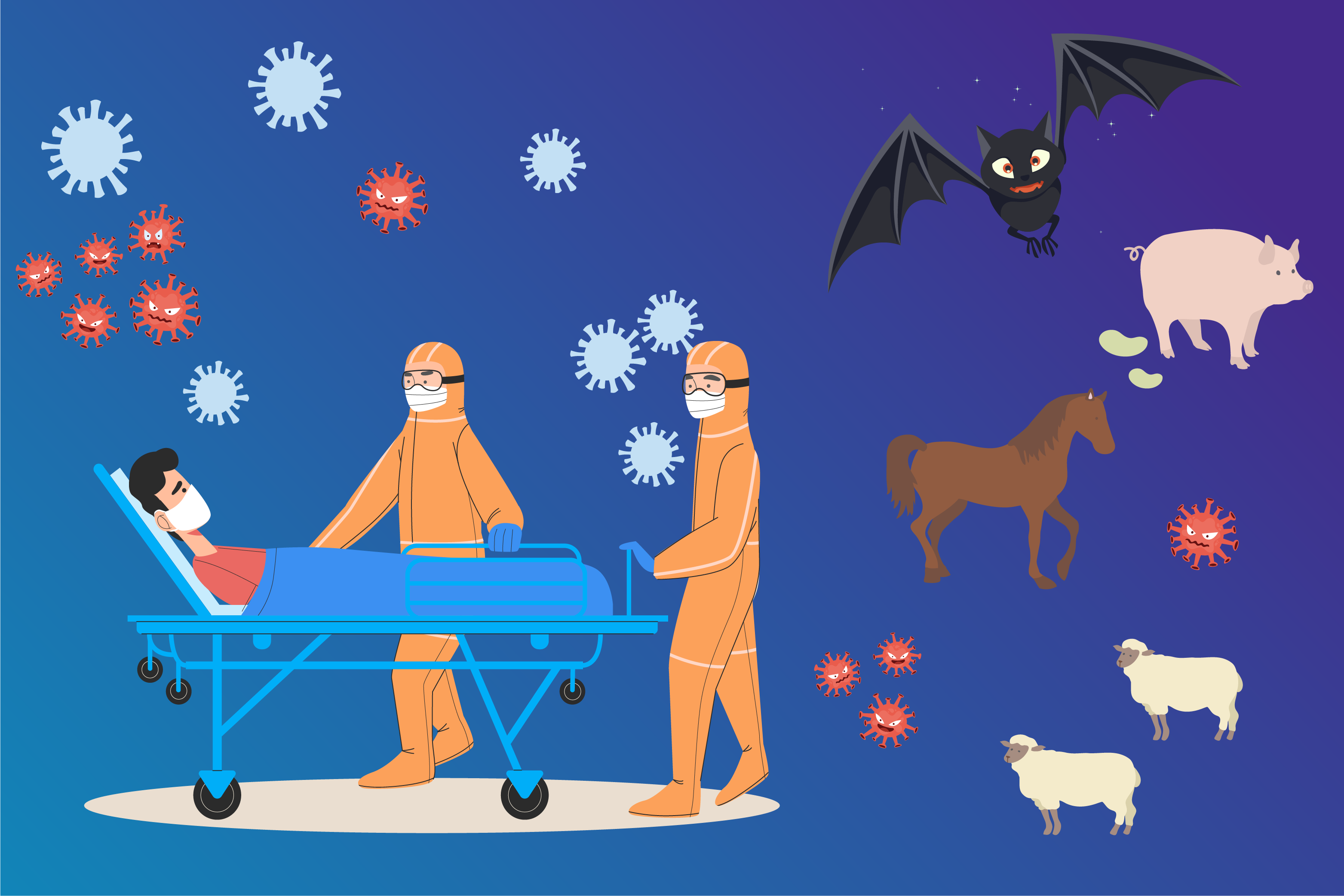

01 Outbreak Resurfaces: How Dangerous Is Nipah Virus?
Nipah virus is an RNA virus that belongs to the family Paramyxoviridae . It can attack the lungs and brain, causing symptoms such as fever, headache, drowsiness, confusion, and coma . The fatality rate among infected individuals can exceed 40%. The incubation period from infection to symptom onset is generally 4 to 14 days , but it can be as long as 45 days . At present, there is no vaccine specifically targeting the Nipah virus and no effective treatment . Since it was first identified in 1998, the virus has triggered multiple outbreaks in South Asia and Southeast Asia , and has been listed by the WHO as a priority emerging zoonotic pathogen of concern. Its high fatality rate, potential for human-to-human transmission , and lack of specific therapeutics make it a “high-risk pathogen” in public health prevention and control.
1.1 Key Transmission Characteristics
(1) Natural reservoir: Fruit bats (flying foxes)
(2) Intermediate hosts: Livestock such as pigs
(3) Routes of human infection:
Contact with bodily fluids from infected animals
Consumption of food contaminated by bats (e.g., date palm sap)
Close person-to-person contact (hospital-acquired transmission has occurred in this outbreak in India)
1.2 Clinical Impact
Nipah virus primarily affects the nervous system and respiratory system , and may cause:
(1) Acute encephalitis ;
(2) Severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) ;
(3) Even among survivors, long-term neurological sequelae may persist.
02 Testing Challenges: Real-World Limitations of Traditional Nucleic Acid Methods
Currently, nucleic acid testing remains the primary approach for confirming Nipah virus infection. However, in real-world outbreak-control settings, traditional methods face multiple constraints.
1️⃣ Single-target design limits robustness to address mutations and co-infections
Conventional PCR assays typically detect a single pathogen or a limited number of targets. In scenarios involving viral mutations or mixed infections with multiple pathogens, there is a higher risk of misclassification or missed detection.
2️⃣ Insufficient sensitivity in early infection
When viral load is low—such as during the incubation period or early-stage infection—traditional methods may fail to consistently detect the virus, potentially delaying the critical window for outbreak control.
3️⃣ Limited support for tracing and evolutionary analysis
PCR results generally provide only a qualitative “positive/negative” outcome and do not generate whole-genome sequence data. As a result, PCR alone cannot adequately support mutation surveillance, transmission-chain tracing, or deeper molecular epidemiology analyses needed for advanced research and outbreak response.
03 Nanodigmbio Solution
With extensive experience in molecular diagnostics and targeted sequencing, Nanodigmbio leverages its proprietary, innovation-driven μCaler hybrid-capture technology and an end-to-end automated platform to build an integrated solution for high-risk pathogens such as Nipah virus—covering rapid detection, precise identification, and in-depth source tracing: the μCaler Pathogen Detection End-to-End Solution (probe customization supported).
This solution delivers a standardized workflow spanning pre-library preparation, targeted capture, data analysis, and result reporting , providing efficient, stable, and scalable technical support for emergency outbreak surveillance and pathogen research.
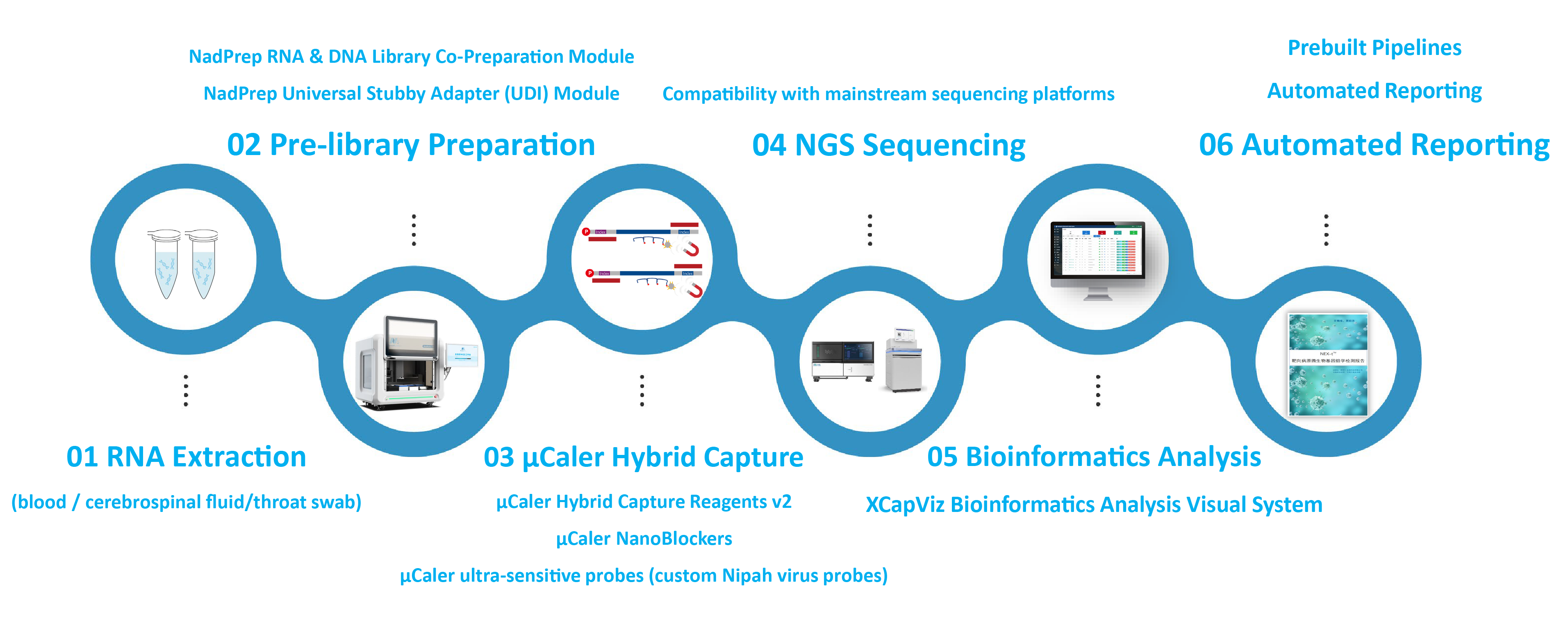
3.1 Core Advantages
✔ High-resolution genotyping and precise identification
Built on a hybrid-capture strategy, the solution enables high-resolution strain genotyping of high-risk pathogens.
✔ Variant tracking capability for target pathogens
Supports targeted coverage of whole genomes or key functional regions, providing a robust data foundation for mutation surveillance and evolutionary analysis.
✔ Reliable detection of low–viral load pathogens
Delivers stable capture performance even for low-abundance pathogens (Ct ≥ 32), helping reduce the risk of false negatives.
✔ Custom probe design for rapid response
Enables tailored probe panels for specific pathogens or application scenarios, allowing flexible and rapid response to emerging and outbreak infectious diseases.
04 Specialized Customization: “Rapid Response” in Outbreak Emergencies
For sudden outbreaks involving high-risk pathogens such as Nipah virus, Nanodigmbio simultaneously provides μCaler professional custom probe design services , offering a strong tool to support outbreak surveillance, research analysis, and public health decision-making.
4.1 Customization Advantages
(1) Single-pathogen whole-genome probe design for efficient coverage of potential variants;
(2) Syndromic screening probe design (e.g., respiratory/neurological), enabling multiplex detection of multiple pathogens;
(3) Rapid delivery and flexible implementation , compatible with mainstream sequencing platforms.
05 Conclusion: Science-Based Prevention and Control—Building a Stronger Health Defense
In responding to emerging and sudden infectious diseases such as the Nipah virus, “early detection, early diagnosis, and early source tracing” are central to interrupting transmission. Leveraging robust targeted sequencing technologies, an end-to-end automated platform, and rapid customization capabilities, Nanodigmbio provides reliable support to public health and disease-control agencies—enabling transmission-chain tracing and viral evolution analysis, and working together to strengthen our health defenses.
Solutions
- Methyl Library Preparation Total Solution
- Sequencing single library on different platform--Universal Stubby Adapter (UDI)
- HRD score Analysis
- Unique Dual Index for MGI platforms
- RNA-Cap Sequencing of Human Respiratory Viruses Including SARS-CoV-2
- Total Solution for RNA-Cap Sequencing
- Total Solution for MGI Platforms
- Whole Exome Sequencing
- Low-frequency Mutation Analysis
Events
-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Boston 2025 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG)

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio Invites You to Join Us at WHX & WHX Labs Kuala Lumpur 2025, Malaysia International Trade and Exhibition Centre in Kuala Lumpur

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio Invites You to Join Us at Hospitalar 2025, Brazil International Medical Device Exhibition in São Paulo

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Denver 2024 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG)

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Sapporo 2024 Annual Meeting of the Japan Society of Human Genetics (JSHG)

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Association for Diagnostics & Laboratory Medicine (ADLM)